Decoding Share Classes in India: Understanding Equity, Preference, and Granting Methods
Navigating SEBI's Framework for Share Classes and Equity Distribution in India
Disclaimer: The content in this post is based on publicly available information and does not reflect our personal views or financial advice. Please consult official SEBI documentation or financial experts for precise guidance.
Navigating the different classes of shares in India can be complex, especially with SEBI regulations ensuring fair practices and investor protection. This guide breaks down key share types, their features, and compliance requirements to help you stay informed.
Types of Shares in India
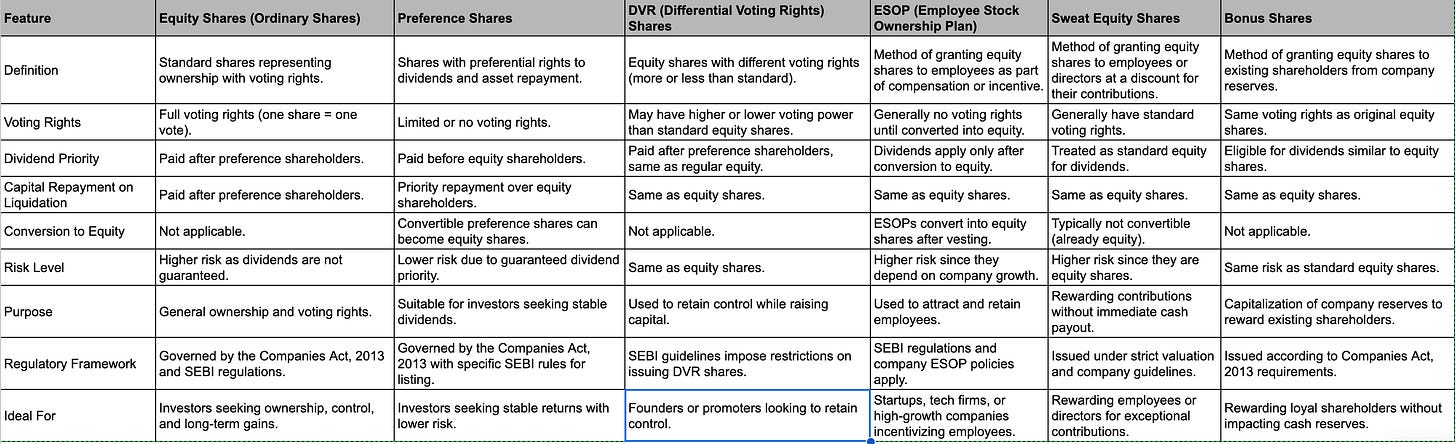
Indian companies can issue various classes of shares to meet different financial and strategic goals. While equity shares, preference shares, and DVR shares are distinct classes of shares, ESOPs, Sweat Equity, and Bonus Shares are methods of granting equity shares, each with specific rules around issuance, vesting, and eligibility. Below is a detailed comparison:
SEBI Compliance Checklist for Each Share Class
1. Equity Shares – SEBI Compliance Checklist
✅ Board Resolution for issuing equity shares.
✅ Shareholder Approval for preferential allotments.
✅ Filing with SEBI: Submit a Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) for IPOs or a Letter of Offer for rights issues.
✅ Minimum Public Shareholding (MPS): Maintain 25% public holding within 3 years of listing.
✅ Allotment Timeline: Complete allotment within 15 days (public issues) or 60 days (preferential issues).
2. Preference Shares – SEBI Compliance Checklist
✅ Board Resolution for issuance.
✅ Shareholder Approval for issuance exceeding authorized capital.
✅ Valuation Report for fair market value assessment.
✅ Redemption Timeline: Must be redeemed within 20 years (30 years for infrastructure companies).
3. Differential Voting Rights (DVR) Shares – SEBI Compliance Checklist
✅ 3 Years Profitability Requirement for issuing DVR shares.
✅ DVR shares cannot exceed 10% of post-issue paid-up capital in IPOs.
✅ Promoter Lock-in: Minimum 26% promoter holding for 3 years.
4. Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) – SEBI Compliance Checklist
✅ Board and Shareholder Approval required before granting ESOPs.
✅ Minimum 1-Year Lock-in for vested shares.
✅ Disclosure Norms: Annual report must include details of ESOP grants.
5. Sweat Equity Shares – SEBI Compliance Checklist
✅ Board and Shareholder Approval for issuance.
✅ Valuation Report for assessing non-cash contributions.
✅ Subject to a 3-year lock-in period.
✅ Cannot exceed 15% of paid-up capital in a year or 25% total paid-up capital.
6. Bonus Shares – SEBI Compliance Checklist
✅ Board Resolution required.
✅ Issued only from free reserves, securities premium, or capital redemption reserves.
✅ Announce a record date for eligibility.
✅ Allotment must be completed within 15 days from the record date.
Final Thoughts
Understanding SEBI's framework for different share classes and equity-granting methods is crucial for both companies and investors. Proper compliance ensures smoother transactions, regulatory adherence, and investor confidence. By following these guidelines, businesses can efficiently raise capital, reward employees, and enhance shareholder value.
References: SEBI official website, Companies Act 2013, SEBI (ICDR) Regulations, SEBI (Share Based Employee Benefits and Sweat Equity) Regulations.